Training and Assessment Delivered on Behalf of Allens Training Pty Ltd RTO 90909
Poisoning First Aid – What To Do While Waiting for Help

Introduction
Every year in Australia, thousands of people are treated for accidental poisoning. Most cases happen in the home, often involving children, but workplaces and outdoor environments carry risks too. Whether it’s a toddler swallowing medicine, a worker exposed to chemicals, or someone inhaling fumes, knowing how to respond quickly and calmly can save lives.
In this guide, we’ll walk through:
- Common causes of poisoning
- First aid steps you can take immediately
- What not to do
- When to call for urgent help
- Prevention strategies for homes and workplaces
And most importantly — the number to remember: Poisons Information Centre – 13 11 26 (available Australia-wide, 24/7).
Common Causes of Poisoning
Poisoning can happen to anyone, anywhere. Understanding the most common causes helps you identify risks and respond effectively.
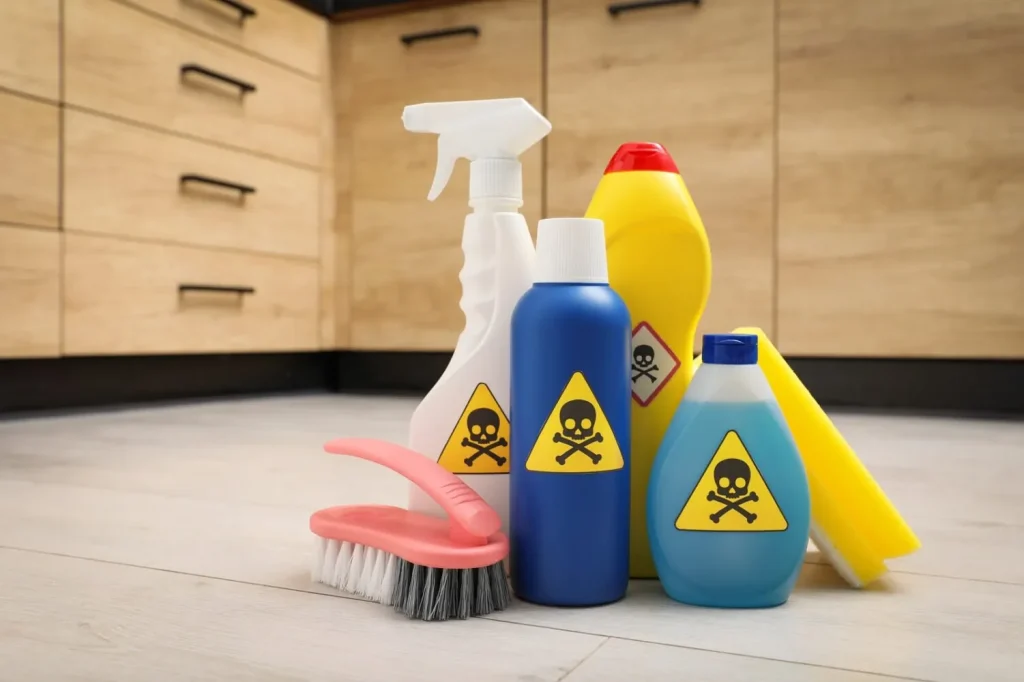
Household Chemicals
- Cleaning products (bleach, oven cleaners, disinfectants)
- Laundry pods and detergents
- Pest control sprays and baits

Medications
- Children mistaking pills for lollies
- Adults accidentally taking a double dose
- Mixing incompatible medications
Plants & Garden
- Toxic plants like oleander, foxglove, or certain mushrooms
- Garden chemicals, weed killers, fertilisers
Food & Drink
- Spoiled or contaminated food
- Excessive alcohol
- Food prepared with unsafe handling practices
Workplace & Outdoor
- Solvents, fuels, or industrial chemicals
- Carbon monoxide poisoning in confined spaces
- Agricultural chemicals (pesticides, insecticides)
General First Aid for Poisoning
No matter the cause, follow these five essential steps:
- Call for advice immediately
- Dial 13 11 26 (Poisons Information Centre) for expert instructions.
- If the person is unconscious, not breathing, or having seizures → call 000 straight away.
- Do not induce vomiting unless directed by professionals. Vomiting can cause further harm.
- Keep evidence – take the bottle, packaging, or plant to show emergency responders.
- Monitor the person’s condition – check for breathing, responsiveness, and signs of deterioration.
- Be ready to provide CPR if they stop breathing. (See our CPR guide for step-by-step instructions).
Specific Situations & First Aid Actions
Swallowed Poisons
- Rinse the mouth gently with water.
- Give small sips of water only if the person is fully conscious.
- Do not give food or milk unless instructed.
Inhaled Poisons (fumes, smoke, gas)
- Move the person into fresh air immediately.
- Loosen tight clothing around neck and chest.
- If breathing is difficult → call 000.
Poison Absorbed Through Skin
- Remove contaminated clothing carefully (wear gloves if available).
- Flush the skin with cool running water for at least 15 minutes.
- Do not apply creams or ointments.
Chemical in the Eye
- Hold the eyelids open and flush the eye continuously with clean, cool running water for 15 minutes.
- Avoid rubbing the eye.
- Seek urgent medical help.
What Not To Do
- ❌ Don’t wait for symptoms to worsen — some poisons act slowly.
- ❌ Don’t give food, milk, or activated charcoal unless directed.
- ❌ Don’t make the person vomit — it may cause burns or block the airway.
- ❌ Don’t leave the person alone, even if they seem “fine”.
When to Call 000 Immediately
Call 000 without delay if the person:
- Is unconscious or hard to wake
- Is having seizures
- Has difficulty breathing or chest pain
- Shows signs of shock (pale, cold, rapid pulse)
- Has burns in the mouth or throat from caustic substances
Even if symptoms seem mild, poisoning can escalate quickly — it’s always better to be safe.
Prevention: Reducing the Risk of Poisoning
Prevention is the best form of first aid. Some simple precautions can dramatically lower the risk:
In the Home
- Lock away medicines and chemicals out of children’s reach.
- Use child-proof caps and safety latches.
- Never store chemicals in drink bottles or food containers.
- Check expiry dates on medicines and safely dispose of old stock.
In the Workplace
- Store chemicals according to WHS regulations.
- Provide clear labelling on all containers.
- Train staff in handling hazardous substances.
- Keep Safety Data Sheets (SDS) accessible.
Outdoors & Garden
- Learn which plants are toxic in your area.
- Wear gloves when handling pesticides or fertilisers.
- Store garden chemicals securely.
Quick Reference Checklist – First Aid for Poisoning
✔ Call 13 11 26 (Poisons Information Centre) for immediate advice.
✔ Call 000 if the person is unconscious, not breathing, or seizing.
✔ Do not induce vomiting.
✔ Rinse mouth with water if swallowed.
✔ Move to fresh air if inhaled.
✔ Flush skin or eyes with running water for 15 minutes if exposed.
✔ Monitor airway, breathing, and circulation.
✔ Be prepared to start CPR if needed.
Conclusion
Poisoning emergencies can be frightening, but with the right knowledge, you can act quickly and effectively.
Every second counts — and being trained in first aid makes you more confident and capable in a crisis.
👉 Ready to build your skills?
Book your First Aid & CPR training with Accidental Health & Safety today and be prepared for the unexpected.



